P Value Of One Sided Test
Hello tess we re glad that you reached out.
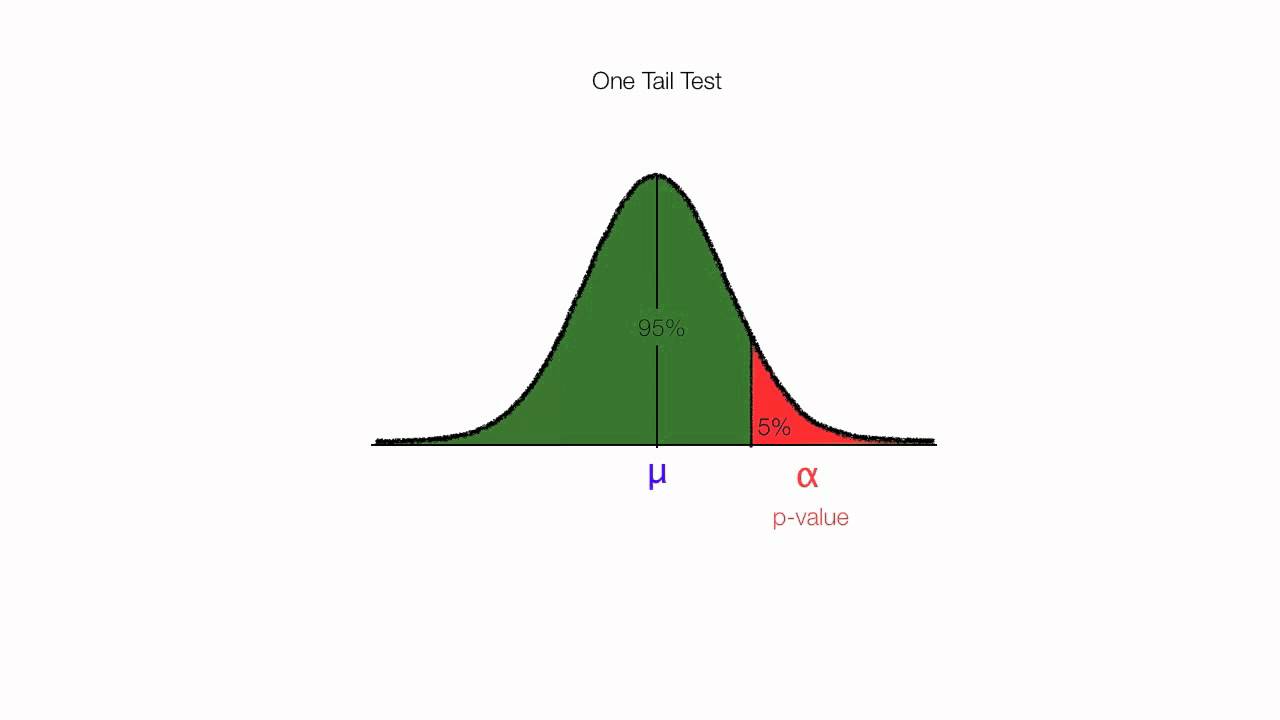
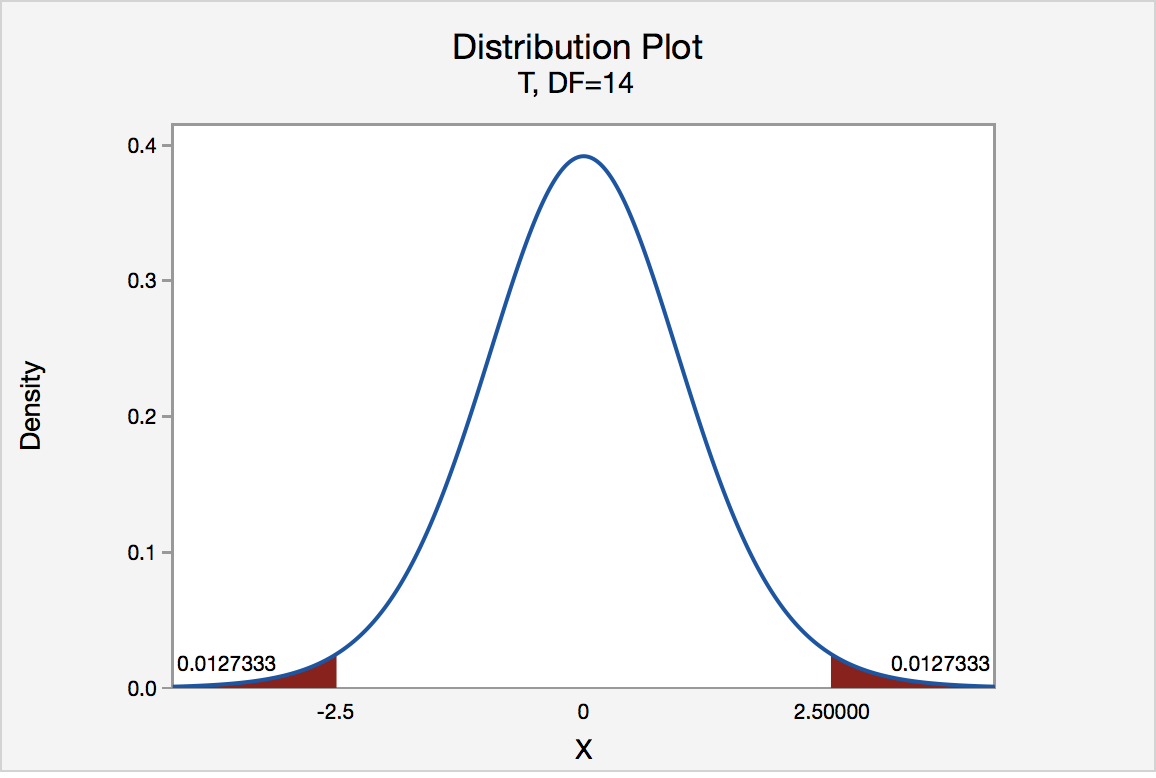
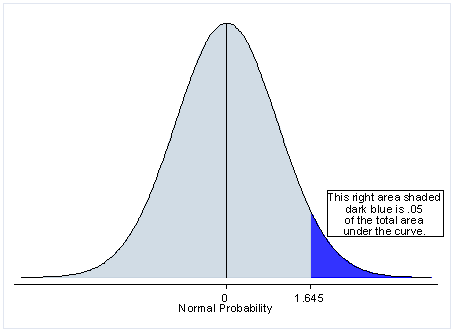
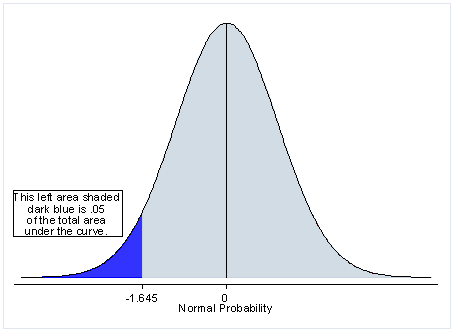
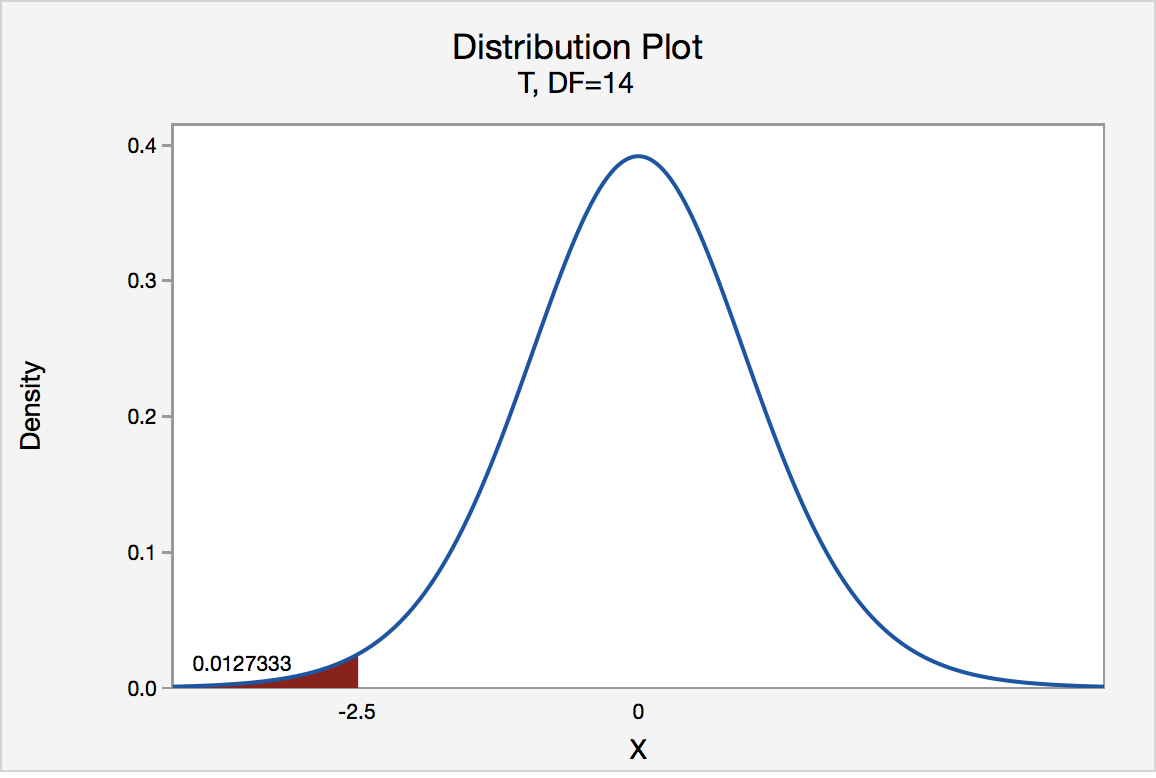
P value of one sided test. If the estimated statistic or median or mean or whatever is in the opposite direction of the alternative hypothesis then the one sided p value will be a large number 1 p 2. If the alternative hypothesis is say for test on one mean ha. The one sided p value is either p 2 or 1 p 2 where p is the printed two sided value. It is true that probability associated with those critical values doubles for the one tailed test 2 5 5 but the critical value itself is not half 2 086 1 725.
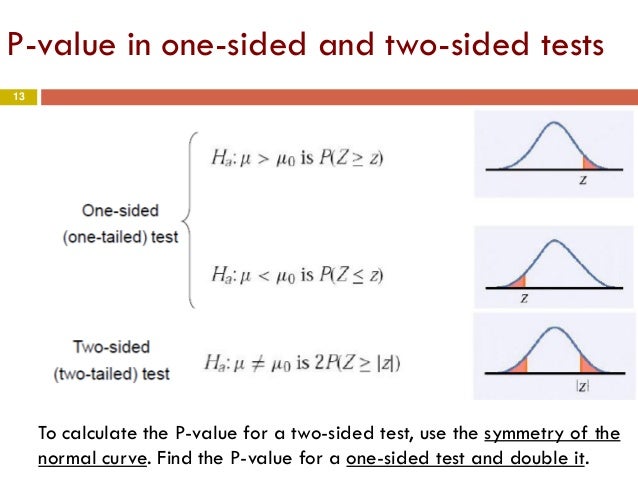
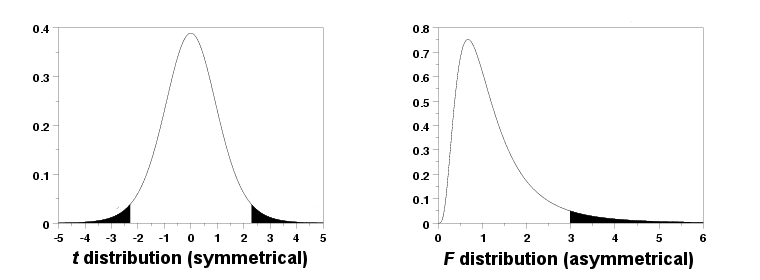
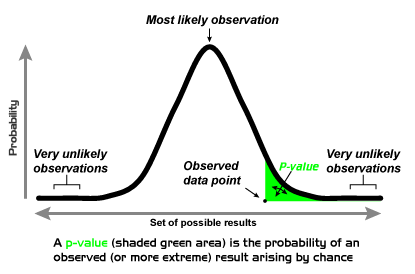
So depending on the direction of the one tailed hypothesis its p value is either 0 5 two tailed p value or 1 0 5 two tailed p value if the test statistic symmetrically distributed about zero. When is it appropriate to use a one sided p value. The p value was introduced by karl pearson in the pearson s chi squared test where he defined p original notation as the probability that the statistic would be at or above a given level this is a one tailed definition and the chi squared distribution is asymmetric only assuming positive or zero values and has only one tail the upper one. You should only choose a one tail p value when both of the following are true.
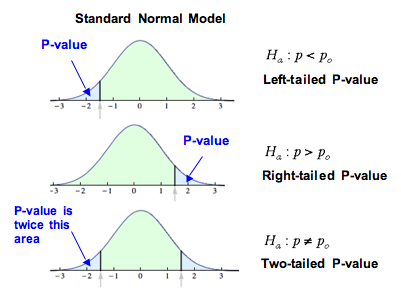
For the p value you can take a two tailed p value and divide by 2 to determine the one sided p value. µ 50 the direction is pointing to the left left tailed test. Study the first several graphs in this article to see why that is true. µ 50 or ha.
A one tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is one sided so that it is either greater than or less than a certain value but not both. µ 50 the direction is to the right right tailed test. µ 50 we have one sided test. In this example the two tailed p value suggests rejecting the null hypothesis of no difference.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Clipboard01-5c94e6b446e0fb00010ae8ed.jpg)